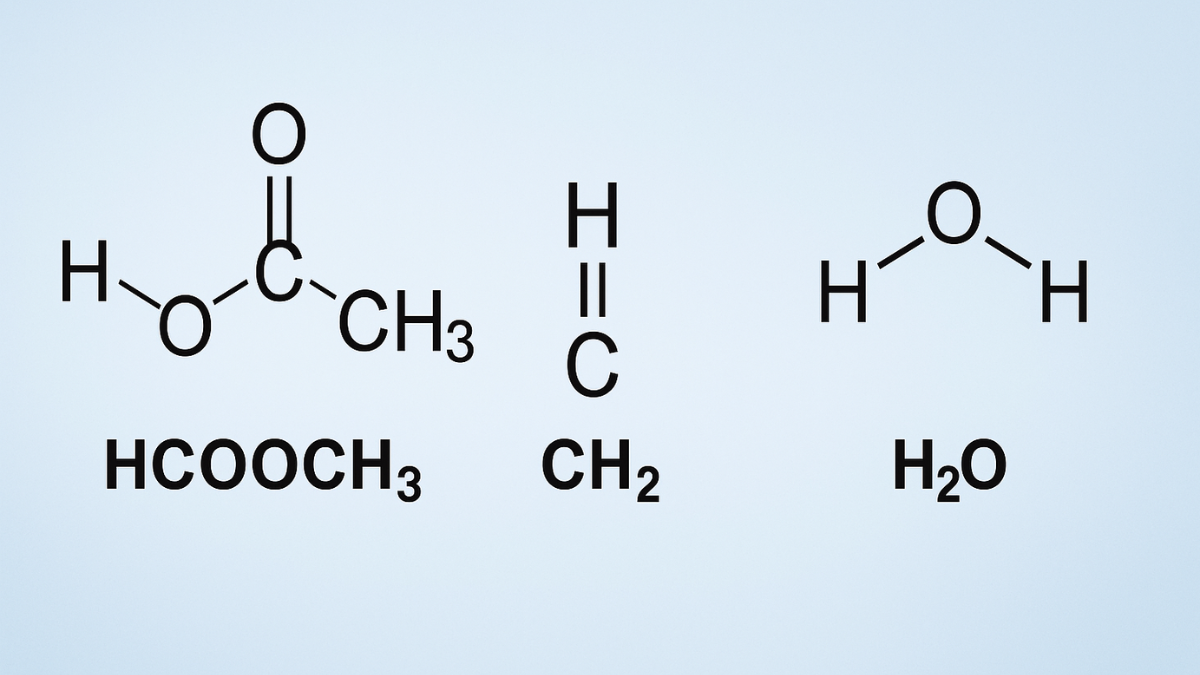
In the field of organic chemistry, understanding how different compounds interact is essential for synthesis, industrial applications, and biological processes. A common combination that often arises in both academic and industrial settings is the interaction of HCOOCH₃ (methyl formate), CH₂ (a reactive methylene group or carbene), and H₂O (water). This article explores their individual properties and how they interact in chemical reactions. We will also cover practical applications, safety, and frequently asked questions to provide a comprehensive understanding of the keyword hcooch ch2 h2o.
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/doge-hhs-migrant-housing-contract/
What is HCOOCH₃?
HCOOCH₃, also known as methyl formate, is the methyl ester of formic acid. It is a colorless, volatile liquid with a pleasant odor and plays a significant role in organic synthesis.
Key Properties of Methyl Formate (HCOOCH₃)
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | HCOOCH₃ |
| Molecular weight | 60.05 g/mol |
| Boiling point | 31.5°C |
| Density | 0.97 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | Slightly soluble |
| Structure | H–C(=O)–O–CH₃ |
Methyl formate is often used as a solvent, intermediate in production of formamide, and in industrial applications including the manufacturing of certain plastics and resins.
Understanding CH₂ in Chemistry
The CH₂ group can refer to a few different chemical species, but most often it is recognized in its carbene form, which is highly reactive. In its singlet or triplet state, CH₂ acts as an intermediate in many reactions.
Forms of CH₂:
- Methylene (CH₂) – A divalent carbon species.
- Carbene (:CH₂) – Highly reactive and short-lived, used in cyclopropanation and insertion reactions.
- Methylene group in chains – A part of alkyl chains in organic molecules.
The context in which CH₂ is mentioned determines its behavior. When combined with HCOOCH₃ and H₂O, the focus is often on reactions involving carbene chemistry or hydration mechanisms.
Role of H₂O (Water) in Organic Reactions
H₂O, or water, is a universal solvent and is involved in numerous organic reactions such as:
- Hydrolysis
- Hydration
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Dehydration reactions (as a leaving group)
Water helps facilitate these reactions due to its polar nature and ability to stabilize ions and transition states.
Reactions Involving HCOOCH₃ + CH₂ + H₂O
When these three compounds interact, several reaction pathways are possible depending on conditions like pH, temperature, presence of catalysts, and reaction medium. Below are some key reaction types:
1. Hydrolysis of Methyl Formate (HCOOCH₃)
Methyl formate undergoes hydrolysis in the presence of water and acid or base catalysts.
Equation:
HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH
In this reaction, methyl formate is broken down into formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol (CH₃OH).
2. Reaction of CH₂ (Carbene) with HCOOCH₃
In the presence of a carbene (CH₂), methyl formate can undergo insertion or cyclopropanation reactions. The carbene might insert into the C–H or C–O bond depending on the catalyst and reaction environment.
3. Overall Possible Reaction with Water Present
In some advanced organic synthesis routes, a reaction mixture containing methyl formate, carbene (CH₂), and water can yield various oxygenated hydrocarbons, alcohols, or esters based on the presence of transition metals or acids.
Mechanism Overview
Let’s break down one mechanism:
- Hydrolysis Step:
- Water attacks the carbonyl carbon of HCOOCH₃.
- Forms a tetrahedral intermediate.
- Methanol leaves; formic acid remains.
- CH₂ Insertion (Hypothetical Pathway):
- Carbene generated via decomposition of diazo compounds.
- Insertion into formic acid or methanol side chain.
- Forms new carbon-carbon or carbon-oxygen bonds.
This complexity underlines the versatility of these molecules when combined in synthetic chemistry.
Real-World Applications
Understanding the reaction between hcooch ch2 h2o has practical implications:
1. Industrial Solvent Production
- Methyl formate is used in manufacturing formamide, which is a precursor to formic acid and methylamine.
2. Polymer and Resin Industries
- Acts as a blowing agent in polyurethane foams.
- Carbene chemistry is crucial in polymer cross-linking.
3. Pharmaceutical Synthesis
- Water-mediated hydrolysis reactions help in drug intermediate preparation.
- Carbene insertions create new molecular frameworks essential for bioactive molecules.
Safety and Handling
Each of these compounds must be handled with care:
- Methyl Formate: Flammable and toxic if inhaled.
- Carbenes (CH₂): Extremely reactive and must be generated under controlled conditions.
- Water: Generally safe but can participate in exothermic reactions.
Always consult MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheets) and follow laboratory safety protocols when working with these chemicals.
Comparative Table: Properties and Roles
| Compound | Formula | Role in Reaction | Reactivity Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methyl Formate | HCOOCH₃ | Ester, hydrolysis substrate | Moderate |
| Carbene | CH₂ | Reactive intermediate | High |
| Water | H₂O | Solvent, hydrolysis agent | Low |
FAQs About HCOOCH₃ + CH₂ + H₂O
- What is the molecular geometry of methyl formate (HCOOCH₃)?
Methyl formate has a bent molecular geometry around the carbonyl carbon and a tetrahedral geometry at the methyl end. - Can CH₂ exist as a stable compound at room temperature?
No, CH₂ as a carbene is highly unstable and exists only as an intermediate under controlled lab conditions. - What happens if you mix methyl formate and water without a catalyst?
Hydrolysis occurs very slowly without an acid or base catalyst. - How is carbene generated in labs for these reactions?
Carbenes like CH₂ are typically generated from diazo compounds or through thermolysis or photolysis. - Does H₂O act only as a solvent in these reactions?
No, water can also act as a reactant, especially in hydrolysis and hydration reactions. - Can methyl formate be synthesized at home?
No, its synthesis involves handling hazardous chemicals and should be done in a professional lab. - What kind of catalysis aids the reaction of CH₂ with HCOOCH₃?
Transition metal catalysts like Rhodium or Copper can facilitate carbene insertion reactions. - Is the hydrolysis of HCOOCH₃ exothermic?
Yes, the reaction releases energy and is mildly exothermic. - Can the combination of these three compounds form a polymer?
Under specific conditions and with other reagents, CH₂ units can contribute to polymer chains. - Are there environmental concerns regarding methyl formate use?
Yes, although considered less harmful than many solvents, it is volatile and should not be released uncontrolled into the environment.
Conclusion
The interaction between HCOOCH₃, CH₂, and H₂O represents a fascinating example of how small molecules with distinct properties can combine in highly useful and complex ways. Methyl formate’s susceptibility to hydrolysis, CH₂’s high reactivity as a carbene, and water’s dual role as a solvent and reactant create opportunities for a wide range of reactions in both synthetic and industrial chemistry. By understanding their behaviors and safety profiles, chemists can harness these molecules for processes ranging from pharmaceutical development to industrial manufacturing. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or chemical enthusiast, grasping the essence of hcooch ch2 h2o chemistry opens doors to innovation and discovery.
also read:https://usaenliinea.com/united-airlines-flight-ua770-emergency-diversion/
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/explore-famousparentingg-com-a-complete-guide-to-trusted-parenting-advice/
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/vidmattapp-the-ultimate-guide-to-downloading-and-enjoying-videos-offline/
also read:https://usaenliinea.com/nhentai-het/
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/en-in-obnews-co/
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/gomyfinance-com-credit-score/
also read:https://usaenliinea.com/doujindesu/