Learn the meaning of Contra Entry in accounting, its types, real-life examples, journal format, and its critical role in cash book transactions. Simple explanations and FAQs included.
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/zuyomernon-system-basketball-the-future-of-strategic-game-play/
What is Contra Entry in Accounting?
In the world of accounting, Contra Entry plays a vital role in maintaining accurate financial records, especially when dealing with both cash and bank transactions within the same business. The term may sound complex, but its concept is quite simple once you understand the basics. This article aims to provide a comprehensive explanation of contra entry, including its definition, examples, format, and why it’s significant in double-entry bookkeeping.
Understanding the Meaning of Contra Entry
Contra Entry refers to a transaction that involves both the cash and bank accounts of the same entity. These transactions are recorded on both the debit and credit sides of the cash book. The term “contra” itself means opposite, which fits perfectly because the effect of the transaction is canceled out within the cash book itself.
Since both the receiving and giving aspects of the transaction occur within the organization’s accounts, it does not impact any external party. These entries are only internal, and no third party is involved in the transaction.
Why is Contra Entry Important?
Contra entry holds great importance in ensuring:
- Accurate cash flow tracking
- Proper reconciliation between cash and bank balances
- Transparency in internal fund movements
By recording contra entries, a business can monitor its internal liquidity management efficiently. These entries are especially useful when preparing bank reconciliations or managing day-to-day financial operations.
Types of Contra Entries
There are two main types of contra entries based on the direction of the transaction:
1. Cash Deposited into Bank (Bank Account Debited, Cash Account Credited)
This occurs when a business deposits physical cash into the bank. For example, if a company deposits ₹10,000 into its bank account, the entry would be:
- Bank A/C Dr. ₹10,000
- To Cash A/C ₹10,000
Here, cash decreases and bank balance increases, and both sides of the transaction are within the business.
2. Cash Withdrawn from Bank for Office Use (Cash Account Debited, Bank Account Credited)
This happens when the business withdraws cash from its bank account to use it directly. Example:
- Cash A/C Dr. ₹5,000
- To Bank A/C ₹5,000
In this case, the cash in hand increases while the bank balance decreases.
Features of Contra Entry
To better understand the significance and nature of contra entries, here are some of their key features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Nature | Internal transaction within the business |
| Accounts Involved | Cash and Bank accounts only |
| Recorded in | Triple Column Cash Book |
| Effect | Cancels out within the cash book |
| Journal Entry | Not needed separately in ledger books |
| Impact on External Parties | None |
| Identification | Marked with “C” in the L.F. (Ledger Folio) column |
This table highlights the internal and non-third-party nature of contra entries, reinforcing their classification as purely internal fund movements.
Format of Contra Entry in Cash Book
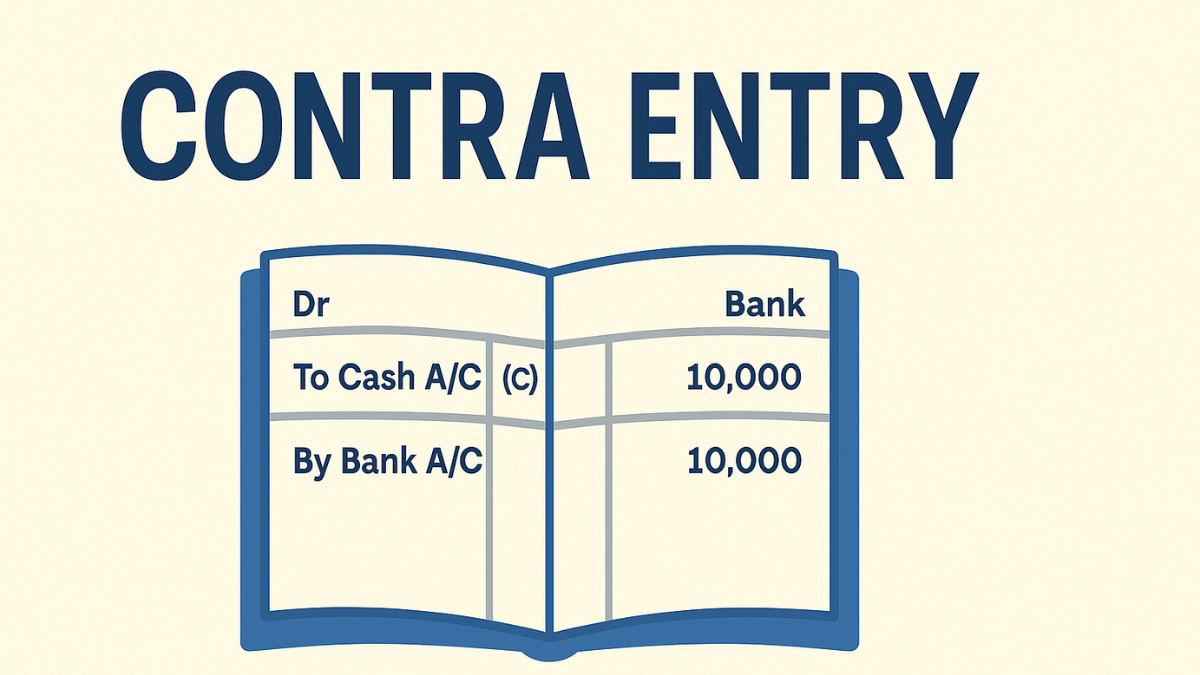
Contra entries are recorded in a Triple Column Cash Book, which includes columns for Cash, Bank, and Discount.
Example Format:
| Date | Particulars | L.F. | Cash (Dr/Cr) | Bank (Dr/Cr) | Discount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01/08/2025 | To Cash A/C (C) | ₹10,000 Dr | |||
| 01/08/2025 | By Bank A/C (C) | ₹10,000 Cr |
In the example above, we deposited ₹10,000 into the bank. The “C” in brackets indicates that it’s a contra entry.
Common Examples of Contra Entry
To illustrate how contra entries work in real-world scenarios, let’s look at a few examples.
Example 1: Depositing Cash into Bank
Transaction: On 1st August 2025, ABC Ltd deposited ₹15,000 cash into its bank account.
Entry in Cash Book:
- Bank A/C Dr. ₹15,000
- To Cash A/C ₹15,000
Marked with (C) on both sides of the cash book.
Example 2: Withdrawing Cash from Bank for Business Use
Transaction: On 2nd August 2025, ₹5,000 withdrawn from bank for office use.
Entry:
- Cash A/C Dr. ₹5,000
- To Bank A/C ₹5,000
Again, marked as (C) because it’s an internal movement of funds.
Differences Between Contra Entry and Other Transactions
To avoid confusion, it’s important to distinguish contra entries from regular accounting transactions. Here’s a comparative view:
| Basis | Contra Entry | Regular Transaction |
|---|---|---|
| Involvement | Only cash and bank accounts | Any two or more different accounts |
| Nature | Internal | May involve external parties |
| Recorded In | Cash Book (both sides) | Journal and Ledger |
| Marking | “C” in L.F. Column | No special marking |
| Impact on Balance Sheet | None | May affect liabilities, assets, etc. |
This comparison helps clarify that contra entries are purely internal and only affect the form (cash/bank) of available funds.
When is a Transaction Not a Contra Entry?
A transaction is not a contra entry if it:
- Involves a third party (like paying a supplier)
- Is a cheque issued or received for sales or purchase
- Includes transfers between different bank accounts (unless both accounts are maintained in the same cash book)
Only direct interactions between cash and bank accounts of the same entity qualify as contra entries.
Role of Contra Entry in Bank Reconciliation
Contra entries help maintain harmony between the cash book and the bank statement. Since they record fund transfers internally, they make it easier to reconcile any discrepancies in bank balances. Without contra entries, it would be challenging to track internal cash/bank transfers accurately.
Common Mistakes in Recording Contra Entries
Some common errors businesses make include:
- Forgetting to mark the transaction with “C”
- Misclassifying third-party transactions as contra
- Recording contra entries in both cash book and ledger unnecessarily
To avoid confusion, ensure only transactions involving cash and bank accounts of the same organization are treated as contra entries.
FAQs About Contra Entry
1. Is contra entry recorded in ledger accounts?
No, contra entries are not posted to the ledger because both debit and credit aspects are already captured in the cash book.
2. Can a cheque received from a customer be a contra entry?
No, because it involves a third party and is not a transfer between the entity’s cash and bank.
3. What does the ‘C’ symbol mean in the cash book?
It denotes that the entry is a contra transaction—an internal cash/bank transfer.
4. Is discount recorded in contra entry?
No, discounts are not part of contra entries as they don’t involve both cash and bank.
5. What if I mistakenly record a contra entry as a regular journal entry?
It can lead to duplication and confusion in reconciliation, affecting financial accuracy.
6. Can contra entry involve two bank accounts?
Only if both bank accounts are part of the same cash book; otherwise, it’s not a contra entry.
7. Is ATM withdrawal a contra entry?
Yes, if it’s for business use and both accounts belong to the business.
8. What’s the effect of contra entry on trial balance?
No net effect, as both debit and credit are within the same accounts.
9. Are online transfers between business bank and cash treated as contra?
Yes, if it’s internal and involves only the business’s own cash and bank.
10. Can contra entries affect profit and loss account?
No, they don’t affect income or expenses, hence no impact on P&L.
Conclusion
Contra entry is a fundamental yet straightforward concept in accounting that deals with internal transactions involving cash and bank accounts of the same business. These entries help maintain clean and accurate financial records and ensure better internal fund management. They’re recorded only in the triple column cash book, marked with a “C” to differentiate them from external transactions.
Understanding how contra entries work, their format, examples, and common errors to avoid can significantly enhance the efficiency of your accounting process. Whether you’re a business owner or a student, mastering this concept is a must for sound financial management.
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/faibloh/
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/skip-the-germs-a-comprehensive-guide-to-healthier-living/
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/florence-elsie-ellis/
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/shani-levni/
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/ttps-docs-google-com-document-pii-deleted/
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/understanding-the-pragmatic-juara100-org-medal-system/
also read: https://usaenliinea.com/thalamovies-com-a-complete-guide-to-the-emerging-movie-streaming-site/